Ways to manage Osteoarthritis of Knee
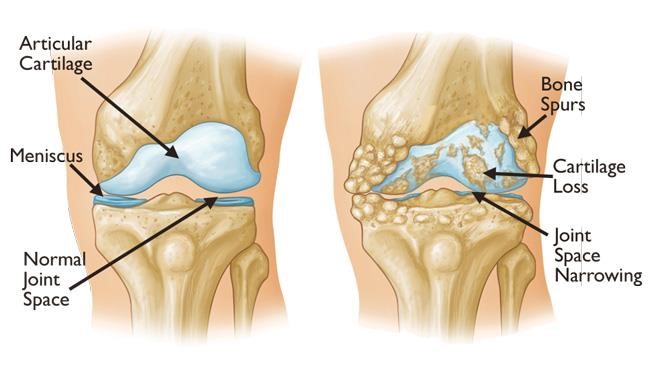
What is Osteoarthritis?
It is a form of degenerative arthritis caused by breakdown of protective cartilage, that acts as a cushion between the bones.Though it can affect any of the joints in our body common ones are Knee, hip,spine and hands.Since in India knee osteoarthritis is most common in the population,we will be discussing in detail.
Treatment for osteoarthritis begins with a combination of physiotherapy for exercises and medication to control pain. In late stages of the disease, surgery is also a possibility.
Symptoms:
- Pain on activity especially worse at nights
- Stiffness in the morning that relieves with mild activity
- Swelling around the joint
- Grating sensation around the joint on activity
- Loss of balance,strength
- Physical Deformity like bowlegged in case of Knee
Causes:
It is a wear and tear disease caused by breakdown of cartilage that helps in non frictional motion between two bones.Osteoarthritis affects the whole joint by causing degeneration the connective tissue that holds the joint together.It also causes inflammation of Joint line.
Risk factors:
- Old age mostly affects people above 50
- Obesity which increases the load on the weight bearing joints
- Women are more likely to be affected
- Post menopausal
- Joint Injuries that occurs during sports activities etc
- Genetics those having family history of bone abnormalities
- Bone deformities
Treatment:
It involves treating the symptoms with medication and physiotherapy, as the cartilage damage cant be reversed non surgically in early stages.In advance stages where the physical activity is restricted with severe deformity,Knee Replacement surgery or other options are recommended.
Role of Physiotherapy:
- To decrease pain and swelling
- To improve strength and mobility
- To improve range of motion
- To improve balance and coordination
- To train patient so as to perform activities of daily living walking, climbing stairs etc with ease
- To improve Gait
- Lifestyle modification
Physiotherapy Treatment includes:
- Use of advanced technology like PEMF, Ultrasound, Short wave Diathermy, TENS to decrease inflammation and pain, cold packs etc
- Active assisted to active exercises for Knee, Hip and ankle
- Strength training exercises for knee musculature to improve co contraction of muscles in order to support the joint
- Weight bearing exercises to improve function and proprioception
- Gait training
- Balance training
Caution:
Please consult a Physiotherapist before you start with exercises for them to evaluate and teach the proper technique. Right supervision will help you heal faster and prevent any injury.Exercises has to be pain free, if any exercise is painful kindly discontinue immediately and see a therapist or medical professional immediately.
Static quadriceps
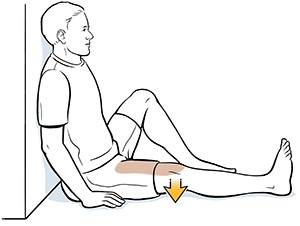
Starting position :- Long sitting or Lying on bed with rolled towel placed under the knee
Movement:- Press knee downwards on the towel trying to tighten the knee cap
Straight Leg raise

Starting position :- Lying on bed with unaffected leg bent at knee with foot resting on the bed
Movement:- Raise the leg from hips with knee straight
Knee sliding
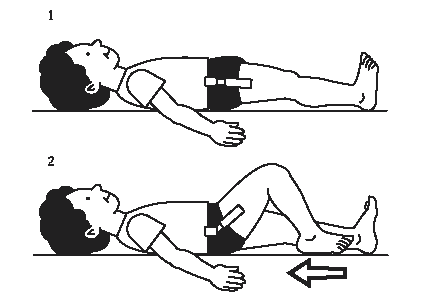
Starting position :- Lying on bed with both legs straight
Movement:- Bend the affected knee by sliding the heel towards hip on the bed
Knee extension

Starting position :- Sitting by edge of chair or bed with thigh rested and knee bent
Movement:- Extending the leg from Knee to make it straight or parallel to ground without lifting the thigh
Wall Squats
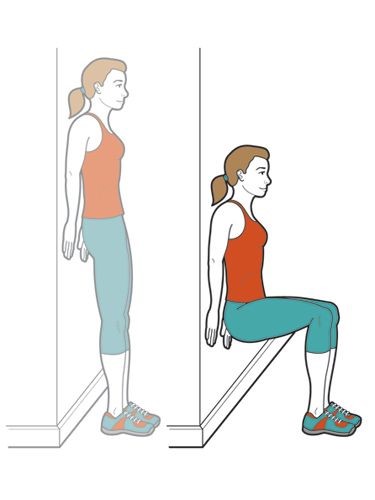
Starting position :- Standing with back touching the wall
Movement:- Squat while sliding against the wall not allowing the knees to move ahead of toes
Repetition:
Each exercise to be done 8-10 times each in pain free range.
Frequency:2-3 times a day
Progression:Resistance can be added depending upon the improvement in strength and pain of the patient which should be decided by certified therapist to prevent any re injury.